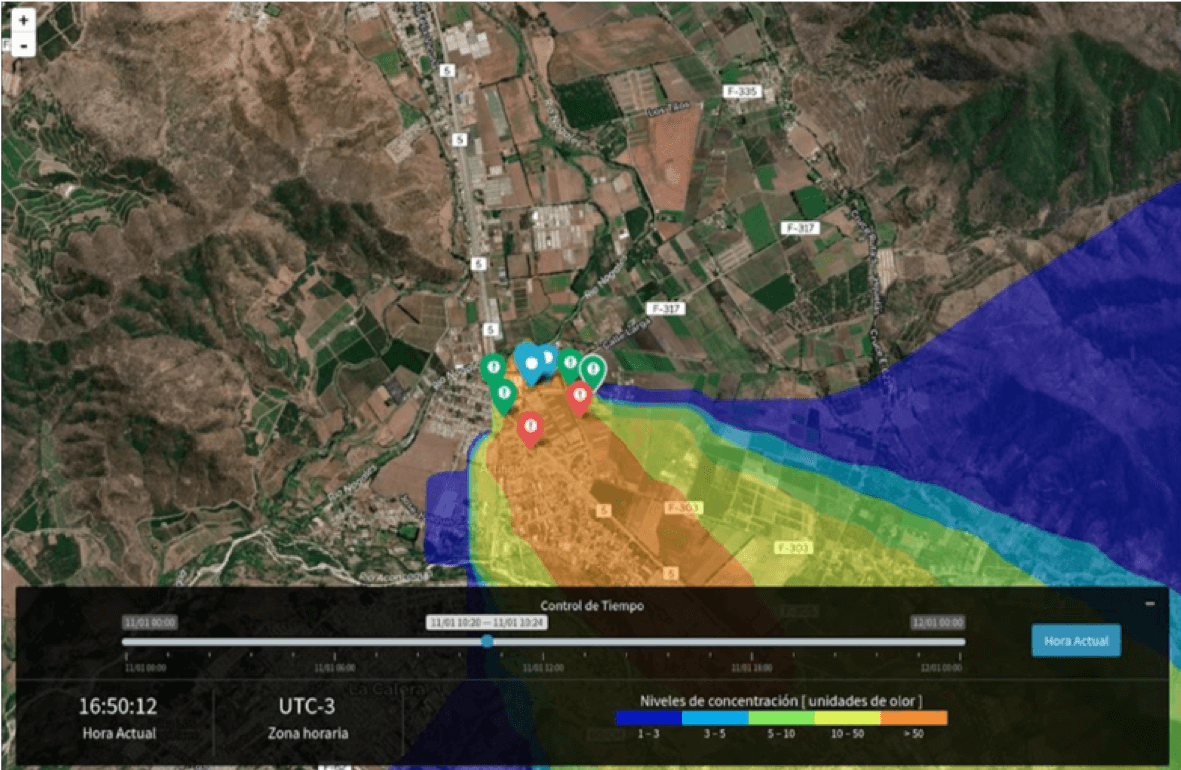
We know that soil pollution causes a chain reaction. It alters soil biodiversity, reducing its organic matter content and its capacity to act as a filter and water stored in the soil and groundwater also becomes contaminated, causing an imbalance in their nutrients.
Through satellite imagery, laboratory tests, and fieldwork, we can contribute to diagnosing the affected areas to develop management plans that allow for the recovery of the affected coverage.